This document describes the data formats used when trading partners exchange invoice information electronically (Norwegian: Elektronisk Handelsformat; EHF). It is prepared as part of the initiative taken by the Norwegian "The Norwegian Agency for Public and Financial Management"" (Difi) within the standardization of electronic trade processes.
|
Reporting bugs
Please use Github Issues to report bugs and lack of content when discovered.
Users currently not registered on Github may create an account for free.
|
Introduction
Background and Objective
The government white paper labeled “St.Meld. nr. 36 (2008-2009) Det gode innkjøp” (The good procurement), states among other things:
It’s the Government’s opinion that increased use of electronic solutions is important to improve and increase the efficiency of public procurement. The use of electronic solutions may reduce time spent on public procurement, increase the competition and arrange for purchases to be more transparent and easier to re-examine. By spending less time and money on procurement, resources will be available for both modernizing the public sector and more welfare. The goal for introducing electronic solutions is to contribute to a better, simpler and more secure procurement.
The previous «Ministry of Government Administration, Reform and Church Affairs» (FAD) considered use of open standards as a vital means to build a well-functioning public administration, with good internal collaboration and a high level of service for both inhabitants and businesses.
An open standard is characterized by its reputation and will be maintained by a non-commercial organization, and the continuing development is based on decision processes open to every interested party. The standard is published and the documentation is available, either free of charge or for a small, insignificant fee. Anyone must be allowed to copy, distribute and use the standard free of charge or for a small, insignificant fee. The intellectual rights related to the standard (e.g. patents) are irrevocably available, without any royalties. There is no reservation regarding re-use of the standard.
The purpose of this document is to describe a common format for invoice messages in the Norwegian market, and to facilitate an efficient implementation and increased use of electronic collaboration regarding the invoicing process based on this format.
Target Audience
The target audience for this implementation guide is both accounting and IT professionals in organizations aiming at performing the invoicing process completely or partially electronic. That means issuing an invoice, a credit note and a reminder. This document may also benefit system suppliers, ERP suppliers and message brokers.
-
Accounting professionals are advised to read chapters 1 through 5.
-
Chapters 5 through 6 are for both accounting professionals as technical implementers
-
IT professionals may concentrate on chapters 7 through 7.
Document Structure
This document consists of the following chapters and contents:
-
Chapter 1 gives a short introduction describing the background and objective of this implementation guide.
-
Chapter 2 gives the change history of the document.
-
Chapter 3 describes the EHF formats (Invoice and Credit note) in general.
-
Chapter 4 links to definitions relevant to EHF formats.
-
Chapter 5 links to general principles and conditions for the formats.
-
Chapter 6 describes in detail central information elements.
-
Chapter 7 deals with validation.
-
Chapter 8 embraces appendices.
1. Changelog
1.1. Consequences of Implementing this version
Version 2.0.17 is a revision of EHF Invoice and Creditnote 2.0, and this version is backwards compatible to EHF Invoice and Creditnote 2.0. This means that any instance documents valid towards EHF Invoice and Creditnote 2.0 is also valid in version 2.0.17. Please note that valid here reflects the validity against the implementation guide of EHF Invoice and Creditnote 2.0, as this is the normative reference.
1.2. Version 2.x
Version 2.0.16 (2019-02-27)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
- |
Fixing syntax, resulting in updated basic validation rules. |
Syntax |
| Validation rules expected to be updated to trigger error in next release: All basic validation rules (EHF-TXX-BXXXXXX). |
Version 2.0.15 (2018-11-15)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
- |
Moving example files into a example file archive. Appendix is updated with the new link. |
Guide |
- |
Replacing listing of validation rules with links to all relevant validation rules. |
Guide |
- |
Combining 'NOGOV-UBL-T10.sch' and 'NONAT-UBL-T10.sch' into 'EHF-UBL-T10.sch'. |
Validator |
- |
Combining 'NOGOV-UBL-T14.sch' and 'NONAT-UBL-T14.sch' into 'EHF-UBL-T14.sch'. |
Validator |
- |
Adding "basic" validation rules automatically created from syntax. Rules are identified as 'EHF-T10-BXXXXX' for Invoice and 'EHF-T14-BXXXXX' for Credit Note where 'XXXXX' is a running number. |
Validator |
| Validation rules expected to be updated to trigger error in next release: All basic validation rules (EHF-TXX-BXXXXXX). |
Version 2.0.14 (2018-09-12)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Adding a missing word in "Profiler og meldinger" section (Norwegian edition only). |
Guide |
Version 2.0.13 (20.02.2018)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Making rules NONAT-T10-R033 (E) and NONAT-T14-R033 (E) trigger as error. |
Validator |
Version 2.0.12 (15.11.2017)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Updating rules NONAT-T10-R031 (F), NONAT-T10-R032 (F), NONAT-T14-R030 (F) and NONAT-T14-R031 (F) from warning to error. |
Validator |
|
For easier maintenance and better transparency use PEPPOL BIS Schematron source in favour of copying generated XSLTs into this project. |
Validator |
|
Replacing rules with rules in EHF Common. |
Validator |
|
Adding rules NONAT-T10-R033 (W) and NONAT-T14-R033 (W). |
Validator |
|
Updated chapter on validation to reflect use of EHF Common. |
Guide |
|
Clarify use of "NA" as order reference and "Your ref". |
Guide |
|
Adding information related to new tax categories valid as of next release. |
Guide |
| Validation rules expected to be updated to trigger error in next release: NONAT-T10-R033, NONAT-T14-R033 |
Mapping of rules for EHF Common in EHF Invoice
| New rule | Description | Old rule |
|---|---|---|
Document in general |
||
EHF-COMMON-R001 (F) |
Document MUST not contain empty elements. |
NONAT-T10-R025 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R002 (F) |
Document MUST not contain empty elements. |
NONAT-T10-R025 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R003 (W) |
Document SHOULD not contain schema location. |
New rule |
EHF-COMMON-R004 (F) |
Document MUST have a syntax identifier. |
NONAT-T10-R019 (F) |
Validation of Norwegian organization numbers |
||
EHF-COMMON-R010 (F) |
MUST be a valid Norwegian organization number. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T10-R026 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R011 (F) |
When scheme is NO:ORGNR, a valid Norwegian organization number must be used. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T10-R036 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R012 (F) |
A VAT number MUST be valid Norwegian organization number (nine numbers) followed by the letters MVA. |
NOGOV-T10-R030 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R013 (F) |
When scheme is NO:ORGNR, a valid Norwegian organization number must be used. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T10-R031 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R014 (F) |
An endpoint identifier scheme MUST have the value 'NO:ORGNR'. |
NOGOV-T10-R027 (F) |
Validation of tax |
||
EHF-COMMON-R020 (F) |
Tax categories MUST be one of the follwoing codes: AA E H K R S Z |
NONAT-T10-R030 (F) |
Formating validation |
||
EHF-COMMON-R030 (F) |
A date must be formatted YYYY-MM-DD. |
NOGOV-T10-R028 (F) |
Validation of other identifiers |
||
EHF-COMMON-R040 (W) |
Invalid GLN number provided. |
NOGOV-T10-R044 (W) |
Code lists |
||
EHF-COMMON-R100 (W) |
Attachment is not a recommended MIMEType. |
NOGOV-T10-R010 (W) |
Mapping of rules for EHF Common in EHF Credit Note
| New rule | Description | Old rule |
|---|---|---|
Document in general |
||
EHF-COMMON-R001 (F) |
Document MUST not contain empty elements. |
NONAT-T14-R023 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R002 (F) |
Document MUST not contain empty elements. |
NONAT-T14-R023 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R003 (W) |
Document SHOULD not contain schema location. |
New rule |
EHF-COMMON-R004 (F) |
Document MUST have a syntax identifier. |
NONAT-T14-R015 (F) |
Validation of Norwegian organization numbers |
||
EHF-COMMON-R010 (F) |
MUST be a valid Norwegian organization number. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T14-R009 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R011 (F) |
When scheme is NO:ORGNR, a valid Norwegian organization number must be used. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T14-R023 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R012 (F) |
A VAT number MUST be valid Norwegian organization number (nine numbers) followed by the letters MVA. |
NOGOV-T14-R013 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R013 (F) |
When scheme is NO:ORGNR, a valid Norwegian organization number must be used. Only numerical value allowed |
NOGOV-T14-R014 (F) |
EHF-COMMON-R014 (F) |
An endpoint identifier scheme MUST have the value 'NO:ORGNR'. |
NOGOV-T14-R010 (F) |
Validation of tax |
||
EHF-COMMON-R020 (F) |
Tax categories MUST be one of the follwoing codes: AA E H K R S Z |
NONAT-T14-R017 (F), NONAT-T14-R028 (F) |
Formating validation |
||
EHF-COMMON-R030 (F) |
A date must be formatted YYYY-MM-DD. |
NOGOV-T14-R011 (F) |
Validation of other identifiers |
||
EHF-COMMON-R040 (W) |
Invalid GLN number provided. |
NOGOV-T14-R044 (W) |
Code lists |
||
EHF-COMMON-R100 (W) |
Attachment is not a recommended MIMEType. |
NOGOV-T14-R020 (W) |
Version 2.0.11 (14.09.2017)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Adding rules NONAT-T10-R031 (W), NONAT-T10-R032 (W), NONAT-T14-R030 (W) and NONAT-T14-R031 (W) for validation of tax categories. |
Validator |
|
Fixing implementation of most rules for higher quality. |
Validator |
|
Changing rule NONAT-T14-R028 (F) from W, replacing NONAT-T10-R028 with NONAT-T10-R030 (F). |
Validator |
|
Changing rules NONAT-T10-R029 (F) and NONAT-T14-R029 (F) from W. |
Validator |
|
Adding rules NOGOV-T10-R044 (W) and NOGOV-T14-R044 (W) for validation of GLN identifiers. |
Validator |
| Validation rules expected to be updated to trigger error in next release: NONAT-T10-R031, NONAT-T10-R032, NONAT-T14-R030, NONAT-T14-R031 |
Version 2.0.10 (15.05.2017)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Updated validation artifacts for PEPPOL BIS from OpenPEPPOL. |
Validator |
|
Updating NONAT-T10-R026 (F) and NONAT-T14-R024 (F) to accept slack of 0.02. Removing NONAT-T10-R027 and NONAT-T14-R025. |
Validator |
|
Adding rules NONAT-T10-R029 (W) og NONAT-T14-R029 (W) for validation of TaxableAmount in TaxSubtotal. |
Validator |
|
Adding information on how to handle non-recommended attachment formats. |
Guide |
|
Updating links in 3.6, 5.7 and code lists. |
Guide |
| Validation rules expected to be updated to trigger error in next release: NONAT-T10-R029, NONAT-T14-R029. |
Version 2.0.9 (15.02.2017)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Changing NOGOV-T10-R041 (F) and NOGOV-T14-R041 (F) from warning to fatal. |
Validator |
|
Adding NOGOV-T10-R043 (W) to validate PayableRoundingAmount to be equal or less than 10% of PayableAmount. |
Validator |
|
Adding information regarding new industry guides for energy and finance. |
Guide |
Version 2.0.8 Hotfix (2016-12-13)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Removing rule implying cac:PaymentMeans/cac:PayeeFinancialAccount/cac:FinancialInstitutionBranch/cbc:ID is mandatory in EHF Core. |
Validator |
|
Removing EHF Core for Invoice and Credit Note. |
Validator |
Version 2.0.8 (15.11.2016)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Adding 6.13.1 describing extended use of consumer invoice (B2C). |
Guide |
|
Adding 6.20 describing payment request variant. |
Guide |
|
Fix minor bug in Invoice and Credit Note example files. |
Attachment |
|
Updating NONAT-T10-R026 (F) and adding 0.01 slack. Introducing NONAT-T10-R027 (W) without slack. |
Validator |
|
Updating NONAT-T14-R024 (F) and adding 0.01 slack. Introducing NONAT-T14-R025 (W) without slack. |
Validator |
|
Fix of NONAT-T10-R014 (F) and NONAT-T10-R021 (F). |
Validator |
|
Fix of NONAT-T14-R017 (F). |
Validator |
|
Fix of NONAT-T14-R004 (F). |
Validator |
|
Changing NOGOV-T10-R034 (F) and NOGOV-T10-R035 (F) from warning to fatal. |
Validator |
|
Changing NOGOV-T14-R021 (F) and NOGOV-T14-R022 (F) from warning to fatal. |
Validator |
|
Changing NOGOV-T10-R041 (F) and NOGOV-T14-R041 (F) from warning to fatal. |
Validator |
|
Updating NOGOV-T10-R026 (F), NOGOV-T10-R030 (F), NOGOV-T10-R031 (F) and NOGOV-T10-R036 (F) to also verify checksum of organization number. |
Validator |
|
Updating NOGOV-T14-R004 (F), NOGOV-T14-R009 (F), NOGOV-T14-R013 (F) and NOGOV-T14-R014 (F) to also verify checksum of organization number. |
Validator |
|
Rule CI-T10-R001 (F) is suppressed in favour of NOGOV-T10-R042 (F). |
Validator |
|
Updated rules NOGOV-T10-R001 (W), NOGOV-T10-R002 (W), NOGOV-T10-R004 (W), NOGOV-T10-R005 (W), NOGOV-T10-R042 (F), NONAT-T10-R001 (F), NONAT-T10-R003 (W), NONAT-T10-R004 (W) and NONAT-T10-R008 (F) to allow document type for internal govermental use. |
Validator |
|
Adding rule NONAT-T10-R028 (W) and NONAT-T14-R028 (W), expected to become F in next release. |
Validator |
|
Updated validation artifacts for PEPPOL BIS from OpenPEPPOL. |
Validator |
|
Change authoritative source of validation artifacts from XSLT to Schematron for NOGOV-T10. |
Validator |
|
Change authoritative source of validation artifacts from XSLT to Schematron for NONAT-T10. |
Validator |
|
Change authoritative source of validation artifacts from XSLT to Schematron for NOGOV-T14. |
Validator |
|
Change authoritative source of validation artifacts from XSLT to Schematron for NONAT-T14. |
Validator |
Version 2.0.7 (15.09.2016)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Converting guide to Asciidoctor format.
|
Guide |
|
Changing rule BII2-T10-R034 to trigger WARNING to allow for negative invoices. |
Validator |
Change of NOGOV-T10-R034 and NOGOV-T10-R035 from warning to error announced earlier for this release is moved to version 2.0.8.
Version 2.0.6 (23.05.2016)
| Issue | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Check to ensure all document level amounts have maximum 2 decimals. |
Validator |
|
Check to ensure a norwegian organisational number is 9 digits if schemeID = NO:ORGNR. |
Validator |
|
Check to verify that if allowance or charge is sent on document level, the element for total allowance or charge exists. |
Validator |
|
Check to verify that only one TaxSubtotal exists per TaxCategory in TaxTotal. Implemented as warning identified as NOGOV-T10-R041 and NOGOV-T14-R041. |
Validator |
|
Changed description of Your ref. |
Guide |
|
Added recommondation that PEPPOL BIS is only used in cases where one of the parties are foreign (cross border trade). |
Guide |
|
Changed text in chapter 6.2 from LineTotalAmount to LineExtensionAmount. |
Guide |
|
Low VAT rate (category AA) changed from 8 to 10%, in chapter 6.6. |
Guide |
Version 2.0.5 (01.09.2015)
| Description | Type |
|---|---|
New validation artefacts for PEPPOL and BII rules, upgrade to XSLT/xPath 2.0. |
Validator |
Empty elements will raise error, not warning as previously, applies to rule NONAT-T10-R025 and NONAT-T14-R023. |
Validator |
Recommondation to use value «NA» if your reference is not relevant for the invoice. |
Guide |
Correct element-naming for payee party in chapter 6.1 |
Guide |
Attachments to implementation guide will be unzipped in Github for easier access to documents |
Attachments |
Missing example files restored |
Attachments |
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
Hotfix (15.04.2015)
Removed validation on schemeID for ClassifiedTaxCatagory for both invoice and creditnote as this was breaking backwards compatibility.
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
Version 2.0.4 (01.03.2015)
-
Added validation on schemeID for ClassifiedTaxCatagory for both invoice and creditnote
-
Warning if attachments are outside recommended types for both invoice and creditnote
-
Correction of example in chapter 6.15
-
Clarifying invoicing to consumers
-
Clarification of use of BBAN when using Norwegian account numbers
-
Editorial changes in chapter 7 and 6.2.2.
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
Version 2.0.3 (01.12.2014)
-
Validation of all mandatory and recommended elements.
-
Validation of elements not used in EHF, and cardinality outside scope of EHF. Validation of datatypes (VAT number, date, bankaccount etc.)
-
Validation of the amount in //cac:TaxTotal/cac:TaxSubtotal/cbc:TaxableAmount.
-
Only organisational numbers are valid in EndpointID.
-
Validation to ensure that the currency attribute is equal to DocumentCurrencyCode.
-
Correction of the validation of TaxInclusiveAmount, Credit note line amount
-
NONAT-T14-R020 changed from error to warning.
-
Adding Dependant to description of elements.
-
Specification of the price element
-
Updated description of Delivery address and date.
-
Fix of typo’s and other small changes to text.
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
-
Yngve Pettersen, Edisys Consuling AS
Version 2.0.2 (29.09.2014)
Change in rule for Sellers VAT number, to allow invoices and credit notes for companies not registered for VAT
Editorial change in appendix 3.
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
Version 2.0.1 (19.08.2014)
Allowing for issue date set to future date for both invoice and credit note. NONAT-T10-R009 and NONAT-T14-R005 changed from Fatal error to warning.
Added rule to check correct use of Profile ID for both Invoice and credit note.
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
Version 2.0 (07.05.2014)
-
Invoice in other currency than NOK
-
Specification of VAT in NOK. The following elements must be filled
-
TaxCurrency Code
-
TaxExchangeRate,
-
Source currency
-
Target currency
-
Exchange rate
-
-
TaxTotal/TaxSubtotal/TransactionCurrencyTaxAmount.
-
-
Added name and address for financial institution
-
New requirements for use of, and content of the attribute listID for codelist elements.
-
Removed the use of attribute schemeAgencyID for CompanyID
-
Removed postal address for VAT representative to harmonize with PEPPOL BIS.
-
OrderReference at document level
Editorial changes for rule ID’s and texts.
-
Olav Kristiansen, Difi
-
Siw Meckelborg, Edisys Consulting AS
-
Jostein Frømyr, Edisys Consulting AS
-
Are Berg, Edisys Consulting AS
-
Trond Bertil Barstad, Edisys Consulting AS
Version 2.0 (30.05.2013)
-
Invoice in other currency than NOK (VAT in NOK)
-
Sellers tax representative
-
Contract type
-
Type AllowanceCharge
-
Contact name for seller and buyer
-
Period, manufacturer and country of origin for the item on line level
-
Registration name for party legal entity, seller and buyer
-
Delivery on document and line level
-
Payment means on document level
-
AllowanceCharge on line level
-
Base quantity for price on line level
-
Reference to invoice/invoice line on line level (BillingReference)
-
Address identifier, PO box, Building number and Department in the Address element , regarding seller, buyer and delivery
-
Countrysubentity in the legal address
-
Department, seller and buyer
-
Payment channel in the payment measns element
-
Contact person, seller and buyer
-
MVA spesifikasjon for rabatter/gebyrer på linje og pris
-
Referance to credtinote on document level (BillingReference)
-
Invoicetype, mandatory
-
Legal registration name, seller and buyer, mandatory
-
VAT percentage on line level, optional
-
Payment terms may occur several times
-
Incorrect VAT category leads to rejection of the document in the validator
-
Content in EndpointID changed
-
Content in UBLVersionID changed from 2.0 to 2.1
-
Content in CustomizationID changed.
-
Version number in Profile ID changed from 1.0 to 2.0
-
Invoicing of consumers (B2C)
-
Accounting cost
-
Delivery
-
Attachments
-
Optional elements
-
EndpointID
-
Bank account number
Use of UBL version 2.1 XML schema.
-
Olav A. Kristiansen, Difi
-
Camilla Bø, Hafslund
-
Morten Gjestad, Nets
-
Dan Andre Nylænder, Unit4 Agresso
-
Jan Terje Kaaby, NARF
-
Morten Krøgenes, Bankenes Standariseringskontor
-
Per Martin Jøraholmen, DFØ
-
Jostein Frømyr, Edisys
-
Erik Gustavsen, Edisys
2. Electronic Commerce Format (EHF)
2.1. About EHF
EHF is an anagram of the Norwegian expression «Elektronisk handelsformat» (Electronic Commerce Format).
EHF is based on the work performed by CEN BII. This is further adjusted to comply with the Norwegian accounting regulations and current practices for the different business processes in the Norwegian market. Difi pursues the goal to cover the full trading process using EHF documents, both before and after awarding (signing of a contract).
Documents, from the tender catalogue to the credit note will be gathered under the EHF umbrella. During 2013 Difi will prepare for the use of EHF formats in what is known as the post award process, i.e. the part of the business process that starts when a supplier and a customer have signed a contract.
By using the EHF documents the collaboration between the supplier and the customer will be predictable. Elements from the tender Catalogue will be re-used in the Order, and elements from the Order will be re-used in the Invoice. This leads to a holistic use of all the documents under the EHF umbrella.
Difi has chosen to use CEN BII as a base for the EHF formats and the Universal Business Language (UBL) as a foundation for the implemented syntax. Both EHF and UBL are open standards and as such not liable to any licensing fees or royalties.
EHF is managed and maintained by Difi.
2.2. Information Consistency
The different EHF formats mentioned above contain a number of common information elements (supplier, customer, item etc.). It is important to preserve consistency in those common information elements, and that means that elements with identical content are declared in the same way and as far as possible given the same element tag name.
EHF invoicing formats will for instance re-use elements from the Catalogue and Order to ensure consistency between the messages and to make sure that the information from the business transactions are reflected in the invoicing documents. This makes it possible to implement an efficient and automated control of the invoice and the originating transactions.
2.3. Empty Elements
The use of empty elements is prohibited in UBL, which is the base for EHF. The reason for this, is that empty elements may be interpreted to have a certain meaning, it could mean that the information was not available at the time of sending as an example. In addition, numeric- and date elements have requirements that would generate validation errors if they were empty.
| The use of empty elements is, for the above mentioned reasons, not allowed in EHF. |
2.4. Message Transport
Open PEPPOL Transport Infrastructure will provide an efficient use and transport of the EHF formats. The objective is to make it easy for parties in different countries to do cross-border trade. Experience shows that it is easy to implement electronic messaging in Norway, because most of the service providers use standard processes.
It must be noted that every document scheduled for this infrastructure must be validated with no fatal errors by Difi’s own validation service. This is likely to be done by the document issuer or by the service provider on behalf of the document issuer.
According to circular P-10/2012 FAD recommends all central government agencies to use this transport infrastructure.
2.5. Profiles and Messages
In line with the underlying methodology for the EHF formats (cf. CEN BII) the electronic messages included in a specific format will be exchanged between the parties as a part of an electronic collaboration process – a profile.
CEN BII has defined a profile as “A specification of how one or more Business Processes are executed by specifying the business rules governing its business collaborations and the information content (data model) of the electronic business transactions exchanged.”
If possible, the EHF is using profiles prepared by BII or PEPPOL. Examples of relevant profiles are:
| Profile | Document types |
|---|---|
Invoice only (bii04) |
Invoice |
Credit note only (biixx) |
Credit note |
Invoice and credit note (bii05) |
Invoice, Credit note |
Invoice, credit note and reminder (biixy) |
Invoice, Credit note, Reminder |
Order and invoice (bii06) |
Order, Order response, Invoice, Credit note |
The messages being exchanged within a profile are customized to comply with the requirements given for that particular business document.
A CustomizationID is used to identify the business rules that apply to the document in question, i.e. the whole set of business rules the document issuer founded the document on.
The example CustomizationID below indicates that the contents of the current message is based on business rules determined by BII (urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns010:ver2.0), extended, customized and clarified by PEPPOL (urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol5a:ver2.0) and further extended, customized and clarified in this implementation guide regarding the Norwegian businesses (urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0).
<cbc:CustomizationID>urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns10:ver2.0:extended:urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol5a:ver2.0:extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0</cbc:CustomizationID>2.6. Use of Collaboration Agreements
The combination of the ELMA registration and the implementation guides referred to in that context eliminates the need for any formal collaboration agreement between the sender and the receiver. The ELMA registration verifies that an actor has declared the ability and the commitment to receive business documents composed according to the specific implementation guide, and any party is free to send the business document to this actor.
Exchanging Catalogue and Order requires no registration in ELMA, and actors are advised to include the use of electronic messages in the purchase contract or to supply an collaboration agreement as an attachment, in order to link the electronic collaboration with the mercantile regulations and thus achieve a regularly revision of the electronic process.
2.7. Versioning
Difi claims the right to exchange the current format with a new one as and when needed. If so, Difi will inform the public via the web site and their registered users via e-mail.
Difi manages the formats in this way:
- Main Version
-
A new main version will be announced at least 5 months prior to release. When a main version is released, there will be at least a 12 months implementation period before the new version is made mandatory.
Difi intends to relate every main version to the regulations concerning IT standards in the public sector.
- Sub Version
-
A new sub version will be announced at least 3 months prior to release and is made mandatory 5 months after release.
All sub versions must be backwards compatible. 2 months after the new sub version has become mandatory, the support (validation service and implementation guide) is ceased for preceding versions.
- Revision
-
A revision is in principle a result of bug fixing the latest sub version, and will be announced at release time and should be implemented without further delay.
3. Definitions
- Supplier
-
Person or company supplying goods or services on own or someone else’s behalf.
- Seller
-
Person or organisation with the necessary authority to sign a contract and transfer the ownership of a product or service.
- Customer
-
Person or organisation acquiring the ownership of a product or a service against agreed price and payment terms.
- Buyer
-
Person or organisation acquiring the ownership of a product or a service for an agreed price and payment terms.
- Invoice
-
A commercial document confirming a sale between a seller and a buyer. The invoice is issued by the seller and the buyer has to pay the claim.
- Electronic invoice
-
An invoice transferred electronically from the issuer to the receiver. The invoice is imported into and processed by the receiver’s computerized accounting system.
- Invoice issuer
-
Person or organisation that issues an invoice.
- Invoice receiver
-
Person or organisation that receives an invoice.
- Payment receiver
-
Person or organisation that receives the payment.
- Credit note
-
A commercial document cancelling all or part of an invoice already issued. The Credit note must have a distinct reference to the originating invoice.
- Electronic Credit note
-
A credit note transferred electronically from the issuer to the receiver. The credit note is imported into and processed by the receiver’s computerized accounting system.
4. Principles and Prerequisites
This chapter describes the principles and assumptions that underlie the use of EHF invoicing process. This is basically similar to the CEN BII 05 Billing profile.
4.1. Invoice Messages in General
The electronic messages described in this implementation guide are Invoice and Credit note. The messages make it possible for the supplier to issue an invoice, send it to the customer and receive the agreed payment.
4.2. Functionality and Roles
The diagram below shows the roles involved in the invoicing process. In EHF, the customer and invoice recipient is the same entity, as is the supplier and the invoice issuer.
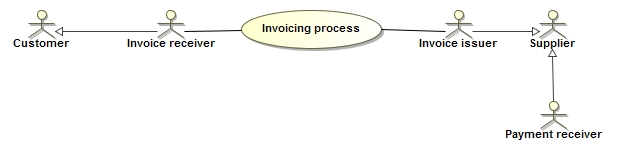
4.3. Profiles and messages
All messages contains ProfileID and CustomizationID. ProfileID identifies what business process a given message is part of, and CustomizationID identifies the kind of message and the rules applied.
Profiles are connected to one business process, and may contain multiple document types. Valid document instances must contain corresponding ProfileID and CustomizationID.
The listing below are related document types connected to the role of receiver in the conversation. Registration in ELMA describes the receivers capabilities.
| CustomizationID is a string without spaces. The list below contains spaces in CustomizationID to make them easier to read. Make sure to remove any spaces before use. |
4.3.1. Profile 04 - Invoice Only
- ProfileID
-
urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:bii04:ver2.0
| Type | CustomizationID | Role |
|---|---|---|
Invoice |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns010:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol4a:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
4.3.2. Profile 05 - Invoice and Credit Note
- ProfileID
-
urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:bii05:ver2.0
| Type | CustomizationID | Role |
|---|---|---|
Invoice |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns010:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol5a:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
Credit Note |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns014:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol5a:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:kreditnota:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
4.3.3. Profile XX - Credit Note Only
- ProfileID
-
urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:biixx:ver2.0
| Type | CustomizationID | Role |
|---|---|---|
Credit Note |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns014:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:biixx:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:kreditnota:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
4.3.4. Profile XY - Invoice, Credit Note and Reminder
- ProfileID
-
urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:biixy:ver2.0
| Type | CustomizationID | Role |
|---|---|---|
Invoice |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns010:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile.eu:biixy:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
Credit Note |
urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns014:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:biixy:ver2.0 :extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:kreditnota:ver2.0 |
Contracting Authority |
Reminder |
NA |
Contracting Authority |
4.4. Use of UBL 2.1
This version of EHF Invoice and Creditnote is based on UBL XML schema version 2.1. Previous versions of the EHF Invoice and Creditnote used UBL version 2.0.
4.5. The Invoicing Process
The invoicing process includes issuing and sending the Invoice and the Credit note from the Supplier to the Customer and the reception and handling of the same at the customer’s site.
The invoicing process is shown in this work flow: 1. A Supplier issues and sends an EHF Invoice to a Customer. The invoice refers to one or more orders and a specification of delivered goods and services. An invoice may also refer to a contract or a frame agreement. The invoice may specify articles (goods and services) with article number or article description. 1. The Customer receives the invoice and processes it in the invoice control system leading to one of the following results: 1. The Customer fully approves the invoice, posts it in the accounting system and passes it on to be paid. 1. The Customer completely rejects the invoice, contacts the Supplier and requests a Credit note. 1. The Customer disputes parts of the invoice, contacts the Supplier and requests a Credit note and a new Invoice.
The diagram below shows the invoicing process with the use of EHF invoice messages. This process is based on the profile 5 in CENBII (BII05 - Billing), which assumes that both the invoice and the credit note are exchanged electronically. The profile also includes the message type «Corrective invoice», but this is not used in Norway. If the customer disputes the invoice, the supplier must issue a credit note and a new invoice.
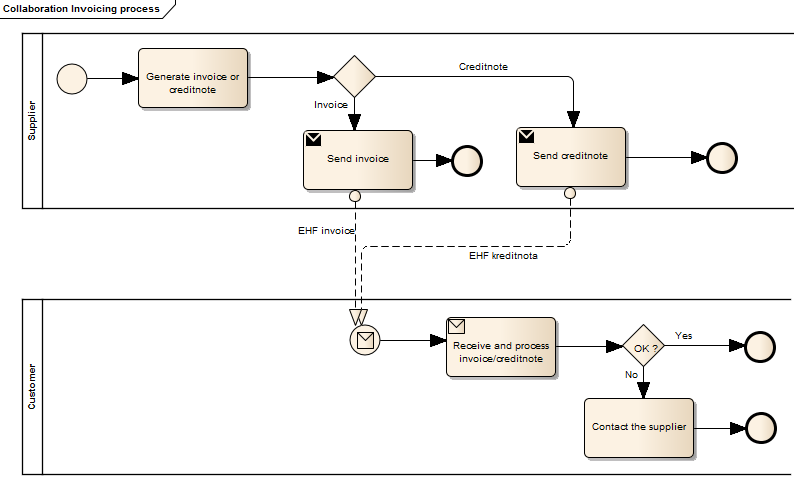
4.5.1. Exception Handling, Validation by the Issuer
An EHF Invoice or EHF Credit note should be validated by the issuer before submitted to the transport infrastructure. The validation process is described in chapter 8. Validation may be performed at several stages and by several services:
-
In the ERP-system. Validation is included in the process that creates the invoice/credit note document. If validation fails the document will not be created. The information the document is based on must be modified and the creation process rerun.
-
In the access point. The service provider offers to validate documents on behalf of the client. If the validation fails the document is returned to the client and not forwarded into the infrastructure. The issuer has in that case 2 options:
-
If the document is not posted in the issuing accounting system, it may be modified and resubmitted.
-
If the document is posted in the issuing accounting system, it cannot be modified. Instead a credit note must be posted (internally) and not submitted. After modifying the data for the invoice a new invoice may be issued.
-
4.5.2. Exception Handling, Validation by the Receiver
Some receivers want to validate incoming documents even though the documents should have been validated before they were submitted to the transport infrastructure. The following scenarios may arise:
-
The document fails to validate:
-
Due to the use of different versions of the EHF formats (cf. chap. 2.1.2), the receiver must process the document manually.
-
Other reasons. The received document is discarded (not processed).The receiver sends a «Message Level Response» to the supplier and requests a new, correct document.
-
-
The document validates correctly, but the receiver disputes all or parts of the contents. The receiver informs the sender manually about the situation. The sender issues a credit note and may issue a new invoice.
4.6. Use of Negative Invoice
Negative invoice is an invoice where the total invoiced amount is less than zero. This version of EHF Invoice accepts that, but Difi’s validation service will give a warning message. Earlier it gave an error message.
A negative invoice must not be confused with a credit note. A negative invoice invoices the sale of new goods or services. A credit note resets or repays all or part of a previously received invoice.
4.7. Financial Advance vs. Account Invoicing
Financial advance is not previously invoiced, ref. «Skattedirektoratets uttalelse av 23.05.07 Finansielle forskudd eller forskuddsfakturering og GBS 13 Forskuddsfakturering.», in English: «Directorate of taxes, statement 23.05.2007: Financial advance or advance billing and GBS13 Advance billing». This means that when the goods or services are delivered an invoice must be issued according to the rules in the Accounting regulations § 5-1 and § 5-2 even if the economic considerations already are levied through financial advance. The invoice settles the financial advance. If the economic considerations exceed the financial advance, the buyer must pay the excessive amount. If the economic considerations are lower than the financial advance, a negative invoice occurs, and the seller must repay the negative invoice amount.
In cases of financial advance or on account invoicing a credit note must be issued following the rules of the "Accounting regulations § 5-2-8" and "GBS 1 Issuing a credit note" to settle the previous invoice (if the specified considerations were too high).
5. Description of Selected Parts of EHF Invoice Messages
This chapter describes selected parts of the information contents of the EHF messages Invoice and Credit note. Go to chapter 7 for the complete information contents.
5.1. Roles and Actor
The following roles may be specified in the format. The same actor may play more than one role depending on the handling routine.
- Seller (AccountingSupplierParty)
-
Seller is mandatory information in EHF.
- Buyer (AccountingCustomerParty)
-
Buyer is mandatory information in EHF.
- Payment receiver (PayeeParty)
-
Payment receiver is optional information in EHF. If this information is not supplied, the seller is the payment receiver.
<cac:AccountingSupplierParty>
<cac:Party>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">123456789</cbc:EndpointID>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="ZZZ">123456</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>Salgsbedriften ASA</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Storgata 34</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Suite 123</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Storevik</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>1234</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>Region A</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:VAT">123456789MVA</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cbc:RegistrationName>Salgsbedriften ASA</cbc:RegistrationName>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:ORGNR" schemeName="Foretaksregisteret">123456789</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:RegistrationAddress>
<cbc:CityName>Storevik</cbc:CityName>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:RegistrationAddress>
</cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cac:Contact>
<cbc:ID>Vår ref</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Name>Ola Nordmann</cbc:Name>
<cbc:Telephone>46211230</cbc:Telephone>
<cbc:Telefax>46211231</cbc:Telefax>
<cbc:ElectronicMail>ola@salgsbedriften.no</cbc:ElectronicMail>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:Party>
</cac:AccountingSupplierParty>
<cac:AccountingCustomerParty>
<cac:Party>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">987654321</cbc:EndpointID>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="GLN">5790000436033</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>AS Innkjøper</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Hovedgata 23</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Bakdøra</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Lillevik</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>8523</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>Region B</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:VAT">987654321MVA</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cbc:RegistrationName>AS Innkjøper</cbc:RegistrationName>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">987654321</cbc:CompanyID>
</cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cac:Contact>
<cbc:ID>3150bdn</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Name>Kari Navnesen</cbc:Name>
<cbc:Telephone>5121230</cbc:Telephone>
<cbc:Telefax>5121231</cbc:Telefax>
<cbc:ElectronicMail>kari.navnesen@innkjoper.no</cbc:ElectronicMail>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:Party>
</cac:AccountingCustomerParty>5.1.1. Customer Number
The customer number is stated in <cac:PartyIdentification>. Specification of the type of party identification used, is stated in the attribute schemeID. The values must be from the PEPPOL Policy of Identifiers.
The most commonly used identifiers in the Norwegian market is:
| SchemeID | Description |
|---|---|
ZZZ |
Issuer unknown, used for internal customer numbers |
GLN |
Global Location Number issued by GS1 |
NO:ORGNR |
Registration in The Brønnøysund Register Centre |
5.2. Allowances and Charges, General Rules
-
Several allowances and charges may be supplied both on header level and line level. For the Price element the validation routine will produce a warning if more than one occurrence of AllowanceCharge is present. The element AllowanceCharge with sub element AllowanceIndicator indicates whether the instance is a charge (true) or an allowance (false).
-
Specification of VAT for allowances and charges, AllowanceCharge/TaxCategory with sub elements, may be supplied both on the header level and on the line level, but not for the Price element. Since allowances and charges on the Price element simply information, there is no VAT calculation on those.
-
The sum of all allowances and charges on the header level must be specified in AllowanceTotalAmount and ChargeTotalAmount respectively (Ref. chap. 6.2.1.1.3).
-
The sum of all allowances and charges on the line level must be taken into account, subtracted or added, when calculating the LineExtensionAmount . These line level allowances and charges must not be calculated into the header level elements.
-
Allowances and charges related to Price shall not be part of any other calculations.
-
Allowances and charges related to Price may specify amount (AllowanceCharge/Amount), base amount (AllowanceCharge/BaseAmount) and a multiplier (AllowanceCharge/MultiplierFactorNumeric).
5.2.1. Invoice
The EHF Invoice format has elements for AllowanceCharge on 3 levels:
-
The header level, applies to the whole invoice and is included in the calculation of the invoice total amount.
-
The line level, applies to the line level and is included in the calculation of the line amount.
-
The line level Price element. Only a way to inform the buyer how the price is set. Is also relevant if the seller or buyer want to post the allowance or charge in their accounting systems. The price itself shall always be the net price, i.e. the base amount reduced/increased with AllowanceCharge/Amount.
Example
-
Net invoice amount exclusive VAT: NOK 3450. 2 invoice lines:
-
Line 1: 10 units of item A. NOK 100 per item and 10% discount.
-
Line 2: 15 units of item B. NOK 200 per item and 15% discount.
-
The price NOK 200 is included the campaign discount of 20% to illustrate the use of AllowanceCharge related to Price.
-
-
-
Total discount: 2 %
-
Invoice charge: NOK 75
-
Shipping cost: NOK 100
XML for Allowances and Charges on the Header Level
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>true</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>Frakt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:Amount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>true</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>Fakturagebyr</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">75.00</cbc:Amount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>2% Totalrabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">69.00</cbc:Amount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>XML for VAT on the Header Level
<cac:TaxTotal>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">889.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cbc:TaxableAmount currencyID="NOK">3556.00</cbc:TaxableAmount>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">889.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:TaxSubtotal>
</cac:TaxTotal>XML for the Header Level Totals
<cac:LegalMonetaryTotal>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">3450.00</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">3556.00</cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount>
<cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">4445.00</cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount>
<cbc:AllowanceTotalAmount currencyID="NOK">69.00</cbc:AllowanceTotalAmount>
<cbc:ChargeTotalAmount currencyID="NOK">175.00</cbc:ChargeTotalAmount>
<cbc:PayableRoundingAmount currencyID="NOK">0.00</cbc:PayableRoundingAmount>
<cbc:PayableAmount currencyID="NOK">4445.00</cbc:PayableAmount>
</cac:LegalMonetaryTotal>XML for Allowances on the Line Level
<cbc:ID>1</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR">10.00</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">900.00</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>10% Rabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge><cbc:ID>2</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR">15.00</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">2550.00</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>15% Rabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">450.00</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>XML for Allowances Releated to Price for Invoice Line 2
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">200.00</cbc:PriceAmount>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>20% Kampanjerabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:MultiplierFactorNumeric>0.200</cbc:MultiplierFactorNumeric>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">50.00</cbc:Amount>
<cbc:BaseAmount currencyID="NOK">250.00</cbc:BaseAmount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
</cac:Price>5.3. Price and Line Amount
Price given for an invoice line is price excluded any allowances or charges on line level, but allowances and charges on price-level is included in the price. See further details on allowance and charge in chapter 6.2.
<cac:InvoiceLine>
<cbc:ID>1</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Note>Scratch on box</cbc:Note>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR" unitCodeListID="UNECERec20">1</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">1273</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:AccountingCost>BookingCode001</cbc:AccountingCost>
<cac:InvoicePeriod>
<cbc:StartDate>2013-06-01</cbc:StartDate>
<cbc:EndDate>2013-06-30</cbc:EndDate>
</cac:InvoicePeriod>
<cac:OrderLineReference>
<cbc:LineID>1</cbc:LineID>
</cac:OrderLineReference>
<cac:AllowanceCharge> (1)
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>true</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>Testing</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">12</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:Item>
<cbc:Description>Processor: Intel Core 2 Duo SU9400 LV</cbc:Description>
<cbc:Name>Laptop computer</cbc:Name>
<cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID>JB007</cbc:ID>
</cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cac:StandardItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="GTIN">1234567890124</cbc:ID>
</cac:StandardItemIdentification>
<cac:CommodityClassification>
<cbc:ItemClassificationCode listID="UNSPSC">12344321</cbc:ItemClassificationCode>
</cac:CommodityClassification>
<cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
</cac:Item>
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">1261</cbc:PriceAmount>
</cac:Price>
</cac:InvoiceLine>| 1 | These charges are at line level, and must be included when calculating the line amount. Line amount= (1*1261)+12 =1273 |
<cac:InvoiceLine>
<cbc:ID>3</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR" unitCodeListID="UNECERec20">2</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">4.96</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:AccountingCost>BookingCode003</cbc:AccountingCost>
<cac:OrderLineReference>
<cbc:LineID>3</cbc:LineID>
</cac:OrderLineReference>
<cac:Item>
<cbc:Name>"Computing for dummies" book</cbc:Name>
<cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID>JB009</cbc:ID>
</cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cac:StandardItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="GTIN">1234567890126</cbc:ID>
</cac:StandardItemIdentification>
<cac:CommodityClassification>
<cbc:ItemClassificationCode listID="UNSPSC">32344324</cbc:ItemClassificationCode>
</cac:CommodityClassification>
<cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">H</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>15</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
</cac:Item>
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">2.48</cbc:PriceAmount>
<cac:AllowanceCharge> (1)
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>Contract</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">0.48</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
</cac:Price>
</cac:InvoiceLine>| 1 | These charges are stated at price level, and shall not be included when calculating the line amount. Line amount = 2.48 * 2 = 4.96 |
5.4. Rounding
-
Rounding shall, as a general rule, be performed on the final result of a calculation only and not on any intermediate calculation, for the result to be mathematically correct.
-
Rounding shall result in a decimal figure with 2 decimal places. The third decimal digit being greater than 4 increases the second decimal digit with 1, whilst the third decimal digit being less than 5 leaves the second decimal digit as it is.
-
The EHF format assumes that all amounts on the header level have a maximum of 2 decimal places. Calculated amounts with more than 2 decimal places, like most VAT calculations, must be rounded. Results from calculations involving already rounded amounts are not subject to rounding , like payable amounts and total amounts included VAT.
5.4.1. Elements That Must be Rounded
-
One line’s total amount, LineExtensionAmount, must be rounded because it may be subject to posting in an accounting system. Note that the elements contained in the LineExtensionAmount (Price * Quantity, Allowances and Charges) must be rounded separately when calculating the LineExtensionAmount. .* All rounded LineExtensionAmount shall be summed as the total line amount on the header level; MonetaryTotal/Line Extension Amount. .* The rounded LineExtensionAmount shall be subject to VAT calculation on the header level; Tax Subtotal/ TaxableAmount.
-
The sum of the header level allowances must be rounded before it is specified to the element MonetaryTotal/AllowanceTotalAmount.
-
The sum of the header level charges must be rounded before it is specified to the element MonetaryTotal/ChargeTotalAmount.
-
The element TaxSubTotal/TaxableAmount which holds the value subject to VAT calculation.
-
The element TaxSubTotal/TaxAmount which holds the VAT value calculated on the d) value.
5.4.2. Rounding of the Payable Amount
It is possible to round the payable amount to the nearest integer. The element MonetaryTotal/PayableRoundingAmount is used for this and is specified on the header level.
This value must be added to the value in MonetaryTotal/TaxInclusiveAmount.
Example: amount 999.81 rounded to 1000. PayableRounding Amount = 0.19.
5.4.3. Examples of Rounding
-
Invoice with 3 lines:
-
Line 1: 24 units of item A. Kr. 51.304 per unit, 10% discount rate. 25% VAT.
-
Line 2: 15 units of item B. Kr. 44.7823 per unit, 15% discount rate. 25 % VAT.
-
Line 3: 21 units of item C. Kr. 134.95 per unit, 24.45 % discount rate. 15% VAT.
-
-
Discount rate on total: 2.35 %
-
Shipping cost: 100.345
-
Prepaid amount: 100
-
Payable rounding amount: -0.36 (note the negative value)
Contents of Amount Elements
| Line | Price | Units | Discount rate | Price*units rounded | Discount rounded | Line total | VAT % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
51,304 |
24 |
10 % |
1231,3 |
123,13 |
1108,17 |
25 % |
2 |
44,7823 |
15 |
15 % |
671,73 |
100,76 |
570,97 |
25 % |
3 |
134,95 |
21 |
24,45 % |
2833,95 |
692,9 |
2141,05 |
15 % |
Total |
3820,19 |
| AllowanceCharge (Invoice) | Values unrounded | |
|---|---|---|
Discount on total (25% mva) |
2,35 % |
89,774465 |
Shipping cost (25% mva) |
100,345 |
| VAT catg. | VAT basis | VAT rate | VAT calculated | VAT per category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
S |
1689,72 |
25 % |
422,43 |
422,43 |
H |
2141,05 |
15 % |
321,1575 |
321,16 |
Total VAT |
3830,77 |
743,5875 |
743,59 |
Sum all lines |
3820,19 |
Invoice total exclusive VAT |
3830,77 |
Invoice total inclusive VAT and rounding |
4574,00 |
Allowances (discount on total) |
89,77 |
Charges (shipping cost) |
100,35 |
Prepaid amount |
100,00 |
Rounding amount |
-0,36 |
Payable amount |
4474,00 |
XML for Allowance and Charges on the Header Level
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>2.35% Totalrabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">89.7744</cbc:Amount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>true</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>Frakt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">100.345</cbc:Amount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>XML for VAT on the Header Level
<cac:TaxTotal>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">743,59</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cbc:TaxableAmount currencyID="NOK">1689.72</cbc:TaxableAmount>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">422.43</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cbc:TaxableAmount currencyID="NOK">2141.05</cbc:TaxableAmount>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">321.16</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">H</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>15.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:TaxSubtotal>
</cac:TaxTotal>XML for Totals on the Header Level
<cac:LegalMonetaryTotal>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">3820.19</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">3830.77</cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount>
<cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">4574.00</cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount>
<cbc:AllowanceTotalAmount currencyID="NOK">89.77</cbc:AllowanceTotalAmount>
<cbc:ChargeTotalAmount currencyID="NOK">100.35</cbc:ChargeTotalAmount>
<cbc:PrepaidAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:PrepaidAmount>
<cbc:PayableRoundingAmount currencyID="NOK">-0.36</cbc:PayableRoundingAmount>
<cbc:PayableAmount currencyID="NOK">4474.00</cbc:PayableAmount>
</cac:LegalMonetaryTotal>XML for Invoice Lines
<cbc:ID>1</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR">24.00</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">1108.17</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:AccountingCost>123</cbc:AccountingCost>
<cac:OrderLineReference>
<cbc:LineID>1</cbc:LineID>
</cac:OrderLineReference>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>10% Rabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">123.1296</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:Item>
<cbc:Name>Vare A</cbc:Name>
<cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID>AAA</cbc:ID>
</cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID=" UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
</cac:Item>
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">51.304</cbc:PriceAmount>
</cac:Price><cbc:ID>2</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR">15.00</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">570.97</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:AccountingCost>123</cbc:AccountingCost>
<cac:OrderLineReference>
<cbc:LineID>2</cbc:LineID>
</cac:OrderLineReference>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>15% Rabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">100.760175</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:Item>
<cbc:Name>Vare B</cbc:Name>
<cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID>BBB</cbc:ID>
</cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID=" UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
</cac:Item>
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">44.7823</cbc:PriceAmount>
</cac:Price><cbc:ID>3</cbc:ID>
<cbc:InvoicedQuantity unitCode="NAR">21.00</cbc:InvoicedQuantity>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">2141.05</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:AccountingCost>123</cbc:AccountingCost>
<cac:OrderLineReference>
<cbc:LineID>2</cbc:LineID>
</cac:OrderLineReference>
<cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cbc:ChargeIndicator>false</cbc:ChargeIndicator>
<cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>24.45% Rabatt</cbc:AllowanceChargeReason>
<cbc:Amount currencyID="NOK">692.9007</cbc:Amount>
</cac:AllowanceCharge>
<cac:Item>
<cbc:Name>Vare C</cbc:Name>
<cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cbc:ID>CCC</cbc:ID>
</cac:SellersItemIdentification>
<cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID=" UNCL5305">H</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>15.00</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
</cac:Item>
<cac:Price>
<cbc:PriceAmount currencyID="NOK">134.95</cbc:PriceAmount>
</cac:Price>5.5. Use of Supplier and Customer Contacts
The customer contact, known as Your ref or “ Deres ref” in Norwegian, is mandatory. The element is used for the reference of who ordered the products/services. Example being the name of the person ordering, employee number or a code identifying this person or department/group. Your ref is often used for internal routing at recipient, and hence it is important to fill this element with the correct values according to the need of the recipient. If this information is not relevant for the invoice, the value “NA” (Not Applicable) should be used, this should be agreed with invoice recipient. Information and is specified in the element AccountingCustomerParty/Party/Contact/ID.
| "Your ref" must be set to "NA" only in situations where such a reference is not provided by customer. When reference is provided by customer must correct element contain the provided reference. |
The supplier contact, known as “Vår ref” in Norwegian, is recommended in EHF. Name/reference/identificator of the person that can answer any questions regarding the invoice/credit note. Information and is specified in the element AccountingSupplierParty/Party/Contact/ID.
5.6. Value Added Tax (Norwegian MVA)
VAT categories used in Norway as of july 1, 2013 are specified in the table below. Use of other VAT categories than those specified below leads to rejection of the XML instance document during validation.
| VAT category | Description | Rate as of January 1, 2016 |
|---|---|---|
S |
Output VAT, regular rate |
25% |
H |
Output VAT, reduced rate, middle |
15% |
R |
Output VAT, reduced rate, raw fish |
11,11% |
AA |
Output VAT, reduced rate, low |
10% |
E |
VAT excempt |
0% |
Z |
VAT excempt (Goods and services not included in the VAT regulations) |
0% |
K |
Emission allowances for private or public businesses – buyer calculates VAT |
0% |
AE |
Reversed VAT |
0% |
G |
Export of goods and services |
0% |
The VAT category must be specified on line level. On the header level both the VAT rate and the category must be specified. In addition the basis for calculating the VAT value, the VAT value itself and the total amount for VAT must be specified on the header level.
Cf. chapter 6.3.3.3 for an XML example regarding VAT.
5.6.1. Currency other than NOK
In cases when invoices are issued in other currencies than the national currency of the seller, the seller may be required to provide information about the VAT total amount in his national currency.
TaxTotal/TaxAmount is given in the DocumentCurrency, whilst the element TransactionCurrencyTaxAmount is used for the tax amount pr. Category in local currency (TaxCurrency). The conversion between DocumentCurrency and TaxCurrency is found in the composite element TaxExchangeRate.
...
<cbc:DocumentCurrencyCode listID="ISO4217">EUR</cbc:DocumentCurrencyCode>
<cbc:TaxCurrencyCode listID="ISO4217">NOK</cbc:TaxCurrencyCode>
...
<cac:TaxExchangeRate>
<cbc:SourceCurrencyCode listID="ISO4217">EUR</cbc:SourceCurrencyCode>
<cbc:TargetCurrencyCode listID="ISO4217">NOK</cbc:TargetCurrencyCode>
<cbc:CalculationRate>8.3804</cbc:CalculationRate>
<cbc:MathematicOperatorCode>Multiply</cbc:MathematicOperatorCode>
<cbc:Date>2014-02-20</cbc:Date>
</cac:TaxExchangeRate>
<cac:TaxTotal>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="EUR">225.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cbc:TaxableAmount currencyID="EUR">900.00</cbc:TaxableAmount>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="EUR">225.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cbc:TransactionCurrencyTaxAmount currencyID="NOK">1885.59</cbc:TransactionCurrencyTaxAmount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">S</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>25</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:TaxSubtotal>
</cac:TaxTotal>
...5.7. Special Taxes/Charges
If special taxes/charges are applicable, each one must be specified on an ordinary invoice line. The only valid tax scheme identifier is «VAT» (code list UN/ECE 5153 subset). If there is no separate line for special tax, the assumption is that the special tax is included in the price.
5.8. Order/Order Number/Order Reference
The customer will issue an order with a unique order number. This unique customer order number must be supplied as the order reference on the invoice.
If the order reference is specified on the header level (OrderReference), the assumption is that the invoice is based on one order only. If order reference is stated at header level, the order reference element on line level is used to state the order line numbers.
<cac:OrderReference>
<cbc:ID>123456</cbc:ID>
</cac:OrderReference>If the invoice is based on more than one order, the order number should be concatenated with the order line number on each invoice line in this way “order number##order line number”. Example: The exact syntax should be agreed upon by the two parties.
If reference numbers other than order- or contract reference (see chapter 6.8) is needed, the additional document references should be used (see chapter 6.11).
When no order reference is provided must the Order Reference element be removed entirely to clearly communicate no order reference was provided. When order reference "NA" is provided is this a actual reference.
| Use of "NA" for "Not Applicable" is not possible as "NA" will be treated as a real order reference. |
5.9. Contract Number
To reference or match an invoice to a signed purchase contract, the contract number could be specified like this:
<cac:ContractDocumentReference>
<cbc:ID>Kontrakt 321</cbc:ID>
<cbc:DocumentTypeCode listID="UNCL1001">2</cbc:DocumentTypeCode>
<cbc:DocumentType>Framework Agreement</cbc:DocumentType>
</cac:ContractDocumentReference>If other references than Order number (ref. ch. 6.7) and Contract number is needed, the element Additional document reference (ref. ch. 6.11) may be used.
5.10. Accounting Information
If the customer wants to automatically post the costs, the accounting information must be transferred to the supplier before or with the order. The supplier should then return the accounting information on the invoice line level.
<cbc:AccountingCost>Prosjekt kostnadskode 123</cbc:AccountingCost>The accounting cost element is just a simple text element. Posting in accounts payable and general ledger often requires several «dimensions». A structured solution regarding content in the accounting cost string has been demanded from a number of stakeholders.
Below you will a proposal regarding content in the account cost string. The structure of the string will be as follows:
-
Format-ID. Fixed text indicating which Chart of Accounts is used. (NS4102 = Norwegain standard)
-
Fieldname. Up to 7 fields may be used:
-
Konto (Account)
-
Avd (Department)
-
Prod (Product)
-
Prosj (Project)
-
MVAkode (VAT code)
-
Dim6
-
Dim7
-
-
Value
-
Separator regarding fieldname and value: Use the ‘=’ character
-
Separator regarding fields: Use the ‘;’ character
Content in general: <Kontoplan>;Konto=<Accountno>;Avd=<Department>;Prod=<Product>;Prosj=<Project>;MVAkode=<VAT code in GL>;Dim6=<Free to use as needed>;Dim7=<Free to use as needed>
Chart of Accounts must always be the first element in the string. No requirements regarding sequence of the other elements. If norwegian standard Chart of Accounts is used by the invoice receiver, then NS4102 must be the leftmost content of the account cost string. For receivers using standard agricultural Chart of Accounts, version 1, the text ‘Landbruk_kontostreng_v01’ must the leftmost content of the accounting cost string. Any other posting requirements than account number, department, product, project and VAT code, may be implemented by using the Dim6 and Dim7 fields. In agricultural context there is a need for a field called ‘driftsgreinkode’. Dim6 may be used in this case.
<cbc:AccountingCost>NS4102;Konto=4010;Avd=25;Prod=5421;Prosj=4098;MVAkode=1</cbc:AccountingCost>5.11. Attachments
Both the invoice and the credit note formats support the use of attachments. The element to hold the attachment information can be repeated multiple times (AdditionalDocumentReference) thus allowing multiple attachments.
Attachments may be used to provide additional information to support the claim represented by the invoice. Additional information can be time sheets, receipts, airfare tickets etc. Attachments are not meant for transferring a pdf-version of the invoice/creditnote. If, however, the “pdf-version” is supplied as an attachment, the element “DocumentType” must specify “Commercial invoice” for an invoice and “Credit note” for a creditnote. Attachments can also be graphs and images. The attachment could be sent as a binary object or as an external address to the object’s storage location (URI).
It is recommended to send additional information included in the format (message) and not as an external address (URI), since many businesses are restricted from pursuing external links. If external link is used, the buyer is committed to download the information contained in the link and store it with reference to the invoice/creditnote document. Such a solution requires according to the Norwegian tax authorities (Skattedirektoratet), an agreement between the parties. Thus use of external links are not recommended.
Additional recommendations:
- Coding
-
Base64
- Document format
-
MIME types:
-
PDF – application / pdf
-
TXT – text / txt
-
GIF – image / gif
-
TIFF – image / tiff
-
JPEG, JPG – image / jpeg
-
PNG – image / png
-
- Size
-
5MB
- Description of attachment
-
It is advised to supply a good description of each attachment and the element to use is: Invoice/Additional_DocumentReference/DocumentReference/DocumentType.
Should only be used for description of the document content.
5.11.1. Copy of the Invoice/Creditnote as an Attachment
There is one special case where it is absolutely required to send the invoice/creditnote as an attachment (cf: FOR 2004-12-01 nr 1558: Forskrift om bokføring). Companies without the ability to send EHF formats will create an invoice or creditnote as usual, e.g. as a document meant to be printed and mailed. Those companies can use an «invoice portal» to register necessary information about the invoice or creditnote and then add a pdf-version or an image of the invoice/creditnote as an attachment. In that case the element DocumentType must specify “Commercial invoice” for an invoice and “Credit note” for a creditnote.
5.11.2. Use of non-recommended attachment formats
Senders may not expect receivers to have support for non-recommended attachment formats except in situations were this is actively agreed upon. If receiver is unable to use received attachments using non-recommended formats must sender resent the business document with updated attachments upon request.
I.e. most computers today support opening HTML files, however not all invoicing systems support handling HTML. In such cases may receiver be seen as unable to handle the format.
5.12. Other Use of Additional Document Reference
The need to distribute information not included in the EHF format arises from time to time. To satisfy this need, the element AdditionalDocumentReference is used. As mentioned above, this element can be repeated multiple times. Examples of information to go into this element are packing lists and the supplier’s order number. Important to notice, there is no code list for this element, and the interactive parties must agree on syntaxes and semantics.
<cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>
<cbc:ID>Doc1</cbc:ID>
<cbc:DocumentType>Timesheet</cbc:DocumentType>
<cac:Attachment>
<cac:ExternalReference>
<cbc:URI>http://www.suppliersite.eu/sheet001.html</cbc:URI>
</cac:ExternalReference>
</cac:Attachment>
</cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>
<cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>
<cbc:ID>Doc2</cbc:ID>
<cbc:DocumentType>Drawing</cbc:DocumentType>
<cac:Attachment>
<cbc:EmbeddedDocumentBinaryObject mimeCode="application/pdf">mimecode</cbc:EmbeddedDocumentBinaryObject>
</cac:Attachment>
</cac:AdditionalDocumentReference><cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>
<cbc:ID>1442316</cbc:ID>
<cbc:DocumentType>Abonnement</cbc:DocumentType>
</cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>5.13. Invoicing of Consumers (B2C)
EHF Invoice 2.0 facilitates invoicing of consumers (B2C). This means that invoice issuers may use the EHF 2.0 format both for business customers and consumers.
Transmission of an invoice to a consumer from an invoice issuer is performed by use of either secure digital post or the consumers «netbank» assuming that the issuer has an agreement.
E-invoice reference must be placed in the ID element of Additional DocumentReference. DocumentType must be set to « elektroniskB2Cfaktura». If secure digital post is used, the personal identity number (fødselsnummer) should be filled in the ID element.
The buyer’s legal entity is not mandatory when “elektroniskB2Cfaktura” is given as documenttype.
<cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>
<cbc:ID>147987</cbc:ID>
<cbc:DocumentType>elektroniskB2Cfaktura</cbc:DocumentType>
</cac:AdditionalDocumentReference>In the consumers market automatic debit (Avtalegiro) is widespread as payment method.
<cac:PaymentMeans>
<cbc:PaymentMeansCode listID="UNCL4461">3</cbc:PaymentMeansCode> (1)
<cbc:PaymentDueDate>2014-07-25</cbc:PaymentDueDate>
<cbc:PaymentID>0265590215686</cbc:PaymentID>
<cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
<cbc:ID schemeID="BBAN">51401099999</cbc:ID>
</cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
</cac:PaymentMeans>| 1 | PaymentMeansCode: 3 (Automated clearing house debit) |
5.13.1. Support for extended usage
As of version 2.0.8 is it possible to use an alternative designation for consumer invoices.
By using value Z01InvoiceTypeCodeZ01elektroniskB2Cfaktura
<cbc:CustomizationID>urn:www.cenbii.eu:transaction:biitrns010:ver2.0:extended:urn:www.peppol.eu:bis:peppol4a:ver2.0:extended:urn:www.difi.no:ehf:faktura:ver2.0</cbc:CustomizationID> (1)
<cbc:ProfileID>urn:www.cenbii.eu:profile:bii04:ver2.0</cbc:ProfileID> (2)
<cbc:ID>42</cbc:ID> (3)
<cbc:IssueDate>2016-11-15</cbc:IssueDate>
<cbc:InvoiceTypeCode listID="UNCL1001">Z01</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode> (4)| 1 | CustomizationID as for normal invoice. |
| 2 | ProfileID as for normal invoice part of profile 04. |
| 3 | Invoice number as for noram invoice. |
| 4 | Use of |
Support for multiple consumer identifiers is made available by using Z01PartyIdentificationZZZschemeID
Use of |
<cac:AccountingCustomerParty>
<cac:Party>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">987654325</cbc:EndpointID> (1)
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="ZZZ">phone:98765432</cbc:ID> (2)
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="ZZZ">pid:12345612345</cbc:ID> (3)
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName> (4)
<cbc:Name>Bob Buyer</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress> (5)
<cbc:StreetName>Anystreet 8</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Back door</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Anytown</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>101</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>RegionB</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:Contact> (6)
<cbc:ID>3150bdn</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Name>John Doe</cbc:Name>
<cbc:Telephone>5121230</cbc:Telephone>
<cbc:Telefax>5121231</cbc:Telefax>
<cbc:ElectronicMail>john@buyercompany.no</cbc:ElectronicMail>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:Party>
</cac:AccountingCustomerParty>| 1 | Endpoint for sending. |
| 2 | Example of use when phone number is used as identifier. |
| 3 | Example of use when social security number is used as identifier. |
| 4 | Name of customer. |
| 5 | Post address of customer. |
| 6 | Contact information of customer. |
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
phone |
Phone number |
pid |
Social security number (requires "databehandleravtale") |
reference |
Common reference |
5.14. Delivery Details (Date and Location)
Delivery details may be given at document (Mandatory) or line level (Optional).
Delivery date should allways be sent, exept for delivery by forwarder, post or the like. See further details in The bookkeeping regulation (bokføringsforskriften) § 5-1-4.
Place of delivery is recommended, and should be sent unless the place of delivery does not affect the ability to ensure the correctness of the invoice. Examples of this can be invoices covering services like investigations and legal assistance. See also NOU 2002:20 point 9.4.1.4.
The delivery element contains an identifer (DeliveryLocation/ID) which may be used if the place of delivery is defined through an identifier. Examples are GLN (Global Location Number) or GSRN (Global Service Relationship Number) both issued by GS1. GSRN is used in the norwegian market for identifying measuring points in the energy sector. Ref. appendix 7.
<cac:Delivery>
<cbc:ActualDeliveryDate>2013-02-15</cbc:ActualDeliveryDate>
<cac:DeliveryLocation>
<cbc:ID schemeID="GSRN">707057500022939815</cbc:ID>
<cac:Address>
<cbc:StreetName>Storgata</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:BuildingNumber>12</cbc:BuildingNumber>
<cbc:CityName>Bergen</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>5000</cbc:PostalZone>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:Address>
</cac:DeliveryLocation>
</cac:Delivery>5.15. Use of Party Tax Scheme for Accounting Supplier Party
PartyTaxScheme under AccountingSupplierParty is an optional element, but according to EU COUNCIL DIRECTIVE 2001/115/ the PartyTaxScheme must be specified if the invoice or the credit note have a VAT total. That means that the element almost always has to be specified. The specification should be the supplier party’s organization number followed by the letters MVA, like this:
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:VAT">123456789MVA</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>5.15.1. Suppliers not registered for VAT
Suppliers that is not registered for VAT, cannot send invoices with VAT amounts > 0. VAT Categories must be set to "Z", and all VAT amounts must be 0,-. The element 'cac:PartyTaxScheme' must be omitted.
<cac:AccountingSupplierParty>
<cac:Party>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">999888777</cbc:EndpointID>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="GLN">1234567898765</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>Bedriften A/S</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Brugt. 10</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Sarpsborg</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>1710</cbc:PostalZone>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cbc:RegistrationName>Supplier without VAT</cbc:RegistrationName>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:ORGNR">999888222</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:RegistrationAddress>
<cbc:CityName>Sarpsborg</cbc:CityName>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode listID="ISO3166-1:Alpha2">NO</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:RegistrationAddress>
</cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cac:Contact>
<cbc:ID>abc1234</cbc:ID>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:Party>
</cac:AccountingSupplierParty><cac:TaxTotal>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">0.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxSubtotal>
<cbc:TaxableAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:TaxableAmount>
<cbc:TaxAmount currencyID="NOK">0.00</cbc:TaxAmount>
<cac:TaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">Z</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>0</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:TaxCategory>
</cac:TaxSubtotal>
</cac:TaxTotal>
<cac:LegalMonetaryTotal>
<cbc:LineExtensionAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:LineExtensionAmount>
<cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:TaxExclusiveAmount>
<cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:TaxInclusiveAmount>
<cbc:PayableAmount currencyID="NOK">100.00</cbc:PayableAmount>
</cac:LegalMonetaryTotal><cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>
<cbc:ID schemeID="UNCL5305">Z</cbc:ID>
<cbc:Percent>0</cbc:Percent>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:ClassifiedTaxCategory>5.16. Bank Account
If both BBAN (Basic Bank Account Number) and IBAN (International Bank Account Number) are available when the XML instance document is generated, the sequence should be BBAN first and IBAN last. If account is Norwegian, BBAN should allways be submitted.
<cac:PaymentMeans>
<cbc:PaymentMeansCode listID="UNCL4461">31</cbc:PaymentMeansCode>
<cbc:PaymentDueDate>2013-06-25</cbc:PaymentDueDate>
<cbc:PaymentID>0265590215686</cbc:PaymentID>
<cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
<cbc:ID schemeID="BBAN">15032387680</cbc:ID>
</cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
</cac:PaymentMeans>
<cac:PaymentMeans>
<cbc:PaymentMeansCode listID="UNCL4461">31</cbc:PaymentMeansCode>
<cbc:PaymentDueDate>2013-06-25</cbc:PaymentDueDate>
<cbc:PaymentID>0265590215686</cbc:PaymentID>
<cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
<cbc:ID schemeID="IBAN">NO7315032387680</cbc:ID>
<cac:FinancialInstitutionBranch>
<cac:FinancialInstitution>
<cbc:ID schemeID="BIC">DNBANOKKXXX</cbc:ID>
</cac:FinancialInstitution>
</cac:FinancialInstitutionBranch>
</cac:PayeeFinancialAccount>
</cac:PaymentMeans>5.17. EndpointID/Legal RegistrationID
Endpoint ID is used for specifying the electronic addresses issuers and receivers are using in their message collaboration. Electronic addresses for norwegian participants in the PEPPOL infrastructure are the legal registration ID of the company and must be registered in ELMA.
Legal registration ID (Company ID) is used for identifying the legal entity the invoice is linked to, ie. the legal entity responsible for the obligation.
Small businesses normally have just one legal registration ID. For these the endpoint ID and the legal registration ID will be compliant.
Major businesses may have several legal registration IDs based on for instance location. If processing of incoming invoices are centralized for all legal entities within the business, the content of the endpoint ID and legal registration ID (Company ID) may be different. In this context it is recommended that all legal entities are registrered in ELMA. Dissemination to a centralized invoice processing function is implemented as part of the registration by the actual accesspoint. (Several invoice receivers share the same endpointID).
The alternative to the solution above is to handle the endpointID as an «invoice receiver address». This means that the invoice receiver manually has to inform the trading partners of the endpointID to use in the message collaboration.
5.18. Tax Representative
Tax representative party for the seller is relevant for sellers delivering goods and services in Norway without having a permanent establishment in Norway. In such cases the name and address of the tax representative must be included in the invoice.
<cac:TaxRepresentativeParty>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>Company name AS</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="NO:VAT">904312347MVA</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>
</cac:TaxRepresentativeParty>5.19. Optional Elements
The receivers invoice handling system must releate to all elements on an invoice (including all optional elements) and at least display all filled elements in the control and verification process of the invoice. Dynamic display of invoice and creditnote based on XML instance documents will be developed by Difi.
6. Validation
To optimize the flexibility in the validation process, each EHF document is validated in different stages with shifting focus in every stage. The pyramid below illustrates the different stages.
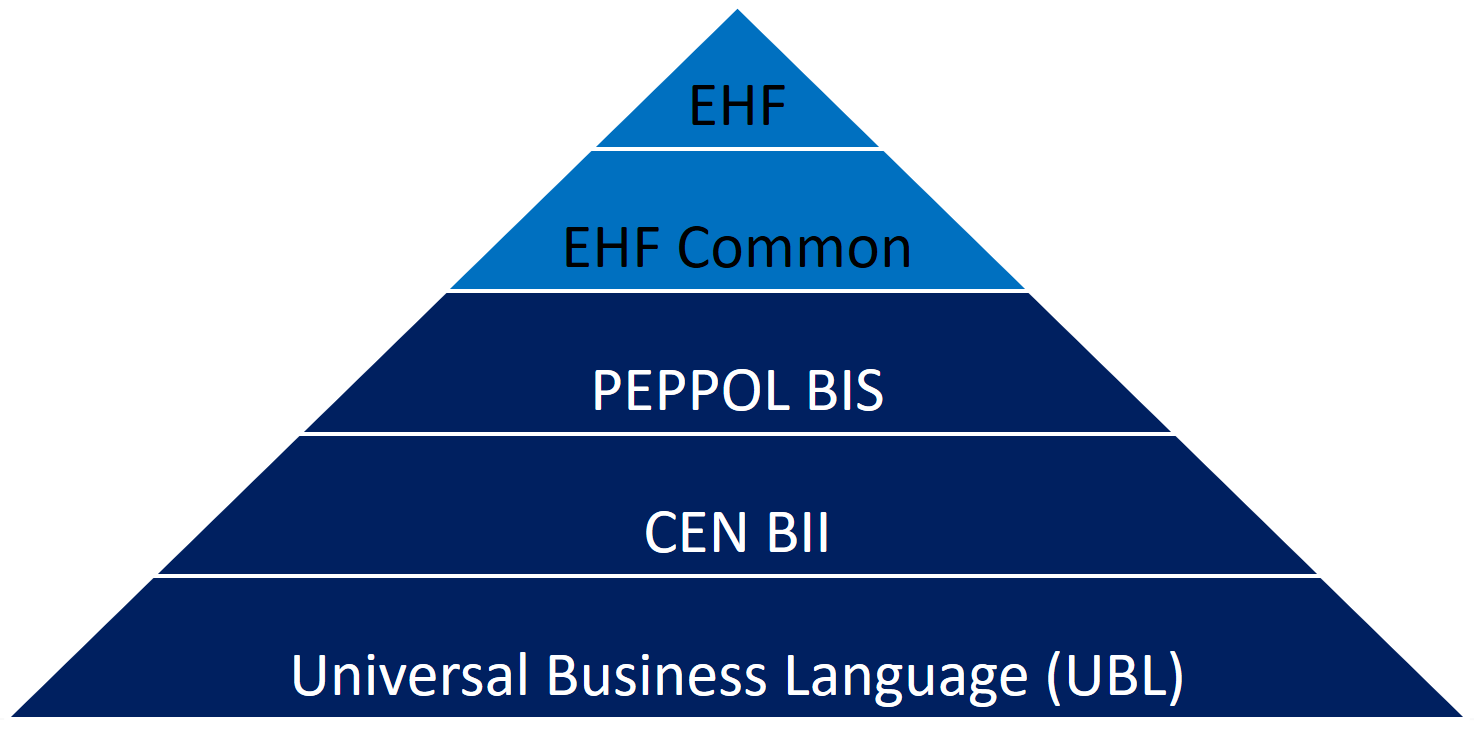
6.1. Validation Principles
Stages in the validation process:
-
Validation of syntax against UBL 2.1 Schema, for example:
-
Tag names and attributes must be correctly written and follow the UBL 2.1 sequence
-
All UBL 2.1 mandatory tag names must be present.
-
The element’s contents must be according to the element’s type definition.
-
-
Validation against CEN BII Core to verify that the message is according to international requirements, like:
-
Valid codes for currencies, countries, tax etc.
-
Mandatory tag names according to CEN BII Core.
-
Logical correlations between information element, i.e. that start date is at least lower than end date, sub totals must be totaled, multiplications give the correct result etc.
-
-
Validation against PEPPOL (EU) rules and regulations
-
Validation against EHF Common rules containing rules common to all EHF document types.
-
Validation against EHF rules and Norwegian legislation, like:
-
Organisation number must be specified for the seller/supplier.
-
«Your ref» must be specified.
-
Addresses, postal zone number and post office/city must be specified for the buyer/customer.
-
6.2. Dynamic Validation
The combination of ProfileID and CustomizationID in an XML document defines the validation rules applied to the document.
CustomizationID may be extended with more elements for specific trade or business validation rules.
6.5. Validation Service
Difi’s Validator is an application program used to validate EHF XML-files.
Further information can be found here: https://vefa.difi.no/ehf/knowledge-base/validation/
7. Appendix
Appendix A: Structure Table
Attached is structure tables providing a structured overview of the document types.
Appendix D: UBL 2.1
This implementation guide builds upon UBL 2.1 Schemas available from OASIS.
These schemas are used when performing syntax validation.
Please see the UBL 2.1 homepage for information about the standard or further resources available.
Appendix E: Schematron
Validation files based on Schematron may be found in our Github repoistory. Release "2021-02-15" is used for the current version of resources and branch "master" is for development and review.
Difi provides validation artifacts as Schematron and not as XSLT as of release 2016-11-15.
Appendix F: Example files
Example files are provided to help implementers. Example files for this implementation guideline is included in the example file archive.